IOC(Inversion of Control)控制反转:所谓控制反转,就是把原先我们代码里面需要实现的对象创建、依赖的代码,反转给容器来帮忙实现。那么必然的我们需要创建一个容器,同时需要一种描述来让容器知道需要创建的对象与对象的关系。这个描述最具体表现就是我们所看到的配置文件。
DI(Dependency Injection)依赖注入:就是指对象是被动接受依赖类而不是自己主动去找,换句话说就是指对象不是从容器中查找它依赖的类,而是在容器实例化对象的时候主动将它依赖的类注入给它。先从我们自己设计这样一个视角来考虑:
1、对象和对象的关系怎么表示?
可以用 xml,properties 文件等语义化配置文件表示。
2、描述对象关系的文件存放在哪里?
可能是 classpath,filesystem,或者是 URL 网络资源,servletContext 等。回到正题,有了配置文件,还需要对配置文件解析。
3、不同的配置文件对对象的描述不一样,如标准的,自定义声明式的,如何统一?
在内部需要有一个统一的关于对象的定义,所有外部的描述都必须转化成统一的描述定义。
4、如何对不同的配置文件进行解析?
需要对不同的配置文件语法,采用不同的解析器。
Spring 核心容器类图
1、BeanFactory
Spring Bean 的创建是典型的工厂模式,这一系列的 Bean 工厂,也即 IOC 容器为开发者管理对象间的依赖关系提供了很多便利和基础服务,在 Spring 中有许多的 IOC 容器的实现供用户选择和使用,其相互关系如下:
public interface BeanFactory {
//对 FactoryBean 的转义定义,因为如果使用 bean 的名字检索 FactoryBean 得到的对象是工厂生成的对象,
//如果需要得到工厂本身,需要转义
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
//根据 bean 的名字,获取在 IOC 容器中得到 bean 实例
Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException;
//根据 bean 的名字和 Class 类型来得到 bean 实例,增加了类型安全验证机制。
<T> T getBean(String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException;
//提供对 bean 的检索,看看是否在 IOC 容器有这个名字的 bean
boolean containsBean(String name);
//根据 bean 名字得到 bean 实例,并同时判断这个 bean 是不是单例
boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, ResolvableType typeToMatch) throws
NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, @Nullable Class<?> typeToMatch) throws
NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
//得到 bean 实例的 Class 类型
@Nullable
Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
//得到 bean 的别名,如果根据别名检索,那么其原名也会被检索出来
String[] getAliases(String name);
}
在 BeanFactory 里只对 IOC 容器的基本行为作了定义,根本不关心你的 Bean 是如何定义怎样加载的。
正如我们只关心工厂里得到什么的产品对象,至于工厂是怎么生产这些对象的,这个基本的接口不关心。
而要知道工厂是如何产生对象的,我们需要看具体的 IOC 容器实现,Spring 提供了许多 IOC 容器的实 现 。 比 如 GenericApplicationContext ,
ClasspathXmlApplicationContext 等 。
ApplicationContext 是 Spring 提供的一个高级的 IOC 容器,它除了能够提供 IOC 容器的基本功能外,还为用户提供了以下的附加服务。从 ApplicationContext 接口的实现,我们看出其特点:
1、支持信息源,可以实现国际化。(实现 MessageSource 接口)
2、访问资源。(实现 ResourcePatternResolver 接口,后面章节会讲到)
3、支持应用事件。(实现 ApplicationEventPublisher 接口)
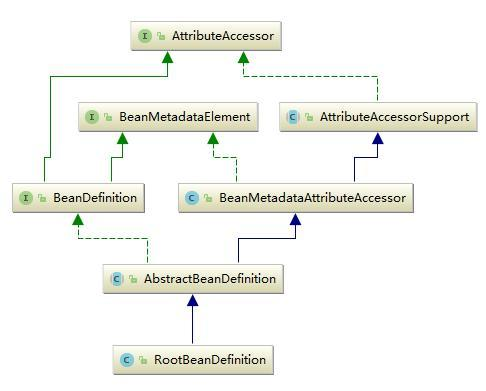
2、BeanDefinition
SpringIOC 容器管理了我们定义的各种 Bean 对象及其相互的关系,Bean 对象在 Spring 实现中是以 BeanDefinition 来描述的,其继承体系如下:
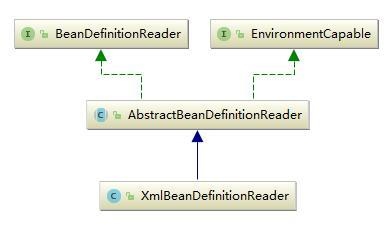
3、BeanDefinitionRe
Bean 的解析过程非常复杂,功能被分的很细,因为这里需要被扩展的地方很多,必须保证有足够的灵活性,以应对可能的变化。Bean 的解析主要就是对 Spring 配置文件的解析。这个解析过程主要通过BeanDefintionReader 来完成,最后看看 Spring 中 BeanDefintionReader 的类结构图:
通过本章内容的分析,我们对 Spring 框架体系有了一个基本的宏观了解,希望小伙伴们好好理解,最好在脑海中形成画面,为以后的学习打下良好的铺垫。
Web IOC 容器初体验
我们还是从大家最熟悉的 DispatcherServlet 开始,我们最先想到的还是 DispatcherServlet 的 init()方法。我们发现在 DispatherServlet 中并没有找到 init()方法。但是经过探索,往上追索在其父类HttpServletBean 中找到了我们想要的 init()方法,如下:
/**
* Map co nfig par ameters onto bean pro perties o f th is servlet, and
* invoke subclas s initialization.
* @throw s Servle tException if bean pr operties are invali d (or requ ired
* proper ties are missing), or if subc lass initialization fail s.
*/
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletExceptio n {
if (logger.isD ebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" getServletName() "'" );
}
// Set bean pr operties from init parameters.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig() ,
this.requiredProp erties);
if (!pvs.isEmp ty()) {
try {
//定位资源
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactor y.forBeanPropertyAcc ess(this );
//加载配置 信息
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext()) ;
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resou rce.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader ,
getEnvironment()) );
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, tru e);
}
cat ch (Bean sException ex) {
if (logg er.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properti es on servl et '" getServletName() "'" , ex) ;
}
throw ex ;
}
}
// Let subclas ses do whatever initialization they like .
initServletBean() ;
if ( logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug( "Servlet '" getServletName() "' configured successfully" ) ;
}
}
在 init()方法中,真正完成初始化容器动作的逻辑其实在 initServletBean()方法中,我们继续跟进initServletBean()中的代码在 FrameworkServlet 类中:
/**
* Overridden method of {@link HttpServletBe an}, invoked after any bean properties
* ha ve been set. Cre ates this servlet' s WebApplicationContext .
*/
@Override
protected final void initServletBean () throw s ServletException {
getServletContext().log( "Initializing Spr ing FrameworkServl et '" getServletName() "'" );
if (this.logge r.isInfoEnabled()) {
tis.logger .info ("FrameworkServlet '" getServletName() "': initialization started" );
}
long startTime = System. currentTimeMillis ();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext() ;
initFrameworkServlet() ;
}
catch (ServletExcep tion ex) {
this.logger .erro r("Context initializat ion failed" , ex) ;
throw ex ;
}
catch (RuntimeExcep tion ex) {
this.logger .erro r("Context initializat ion failed" , ex) ;
throw ex ;
}
if(this.logge r.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System. currentTimeM illis() - startTim e;
this.logger .info ("FrameworkServlet '" getServletName() "': initialization completed in "
elapsedTim e " ms" ) ;
}
}
在上面的代码中终于看到了我们似曾相识的代码
initWebAppplicationContext(),继续跟进:
/**
* Initialize a nd publi sh th e WebApplicationContext for this servlet.
* <p>Delegates to {@li nk #c reateWebApplicationContext} for actual creat ion
* ofthe conte xt. Can be ov erridden in subclasses.
* @return the WebApplicatio nContext instance
* @see #FrameworkServlet(We bApplicationContext)
* @see #setContextClas s
* @see #setContextConfigLoc ation
*/
protected WebApplicationCont ext initWebApplicationContext() {
// 先从 ServletContext 中获得 父容器 WebAppliationContext
WebApplicationContext roo tContext =
WebApplicationContex tUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext()) ;
// 声明子容器
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
// 建立父、子容器之间的关联关 系
if (this.webApplicationCo ntext != null) {
// A conte xt insta nce was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this .webApplicat ionContext;
if (wac instanceof Con figurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebAppli cationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac ;
if (!cwac.isActive() ) {
// T he conte xt ha s not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as c
// s etting t he pa rent context, setting the application contex t id, et
if (cwac.getParen t() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the roo t ap plication context (if any; may be null) as t he paren t
cwac.setParent (rootContext);
}
configureAndRefre shWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
// 先去 ServletContext 中查找 Web容器的引用是否存在,并创建好默认的空 IOC容器
if (wac == nu ll) {
// No cont ext instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has bee n registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it i s assumed
// that th e parent con text (if any) has already been set and that the
// user ha s perfor med any initialization such as setting the conte xt id
wac = findWebApplicati onContext();
}
// 给上一步创建 好的 IOC 容器赋 值
if (wac == null) {
// No context instan ce is defined for this ser vlet -> creat e a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext) ;
}
//触发 onRefresh方法
if (!this.refreshEvent Received) {
// Either the contex t is not a ConfigurableApplicationConte xt with refresh
// support or the co ntext injected at construc tion time had already been
// refreshed -> trig ger initial onRefresh manu ally here.
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContex t) {
// Publish the conte xt as a servle t contex t at tribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeNa me();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName , wac );
if (this.logger.isDe bugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug ("Published WebApplication Context of se rvlet '" getServletName()
"' as Servle tContext attri bute wit h na me [" attrN ame "]");
}
}
return wac;
}
/**
* Retrieve a {@code WebApplicationConte xt} from th e {@code Serv letContext}
* attribute with the {@l ink #setContextAttribut e c onfigured nam e}. The
* {@code WebApplicationC ontext} must ha ve alrea dy been loaded a nd stored in the
* {@code ServletContext} before this se rvlet ge ts initialized ( or invoked).
* <p>Subclasses may over ride this metho d to provid e a different
* {@code WebApplicationC ontext} retriev al strategy .
* @return the WebApplica tionContext for this servl et, or {@code null} if not found
* @see #getContextAttrib ute()
*/
@Nullable
protected WebApplicationC ontext findWebApplicationC ontext() {
String attrName = getContextAttribute ();
if (attrName == null) {
return null;
}
WebApplicationContext wac =
WebApplicationCon textUtils.getWebApplicatio nContext(getServletContext() , attrName) ;
if (wac == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException ("No WebApplicationContext found: initializer not registered?" ) ;
}
return wac ;
}
/**
* Instantiat e the WebApplicationContex t for this servlet, eith er a default
* {@link org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext}
* or a {@lin k #setContextClass cus tom context class} , if set .
* <p>This implementation expec ts custo m contexts to implemen t the
* {@link org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext}
* interface. Can be overridden in subc lasses.
* <p>Do not forget t o register thi s se rvlet instance as applicatio n listener o n t he
* created co ntext (for triggering its {@link #onRefresh callback}, and to call
* {@link org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext#refresh()}
* before returning the context instanc e.
* @param par ent the parent Application Context to use , or {@cod e nu ll} if none
* @return th e WebApplicationContex t fo r this servlet
* @see org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
*/
pro tected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext (@Nullabl e ApplicationContext parent) {
Class<?> contextClass = getContextCl ass();
if (this.l ogger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.log ger.debug( "Servlet wit h na me '" getServletName()
"' will tr y to creat e custom WebApplicationContext conte xt of class '"
contextClass.getName () "'" ", using parent conte xt [ " parent "] ");
}
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationConte xt.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw ne w ApplicationContextExcept ion(
"Fatal initializatio n er ror in servlet wit h nam e ' " getServletName()
"': custom WebApplicationCon text class [" contextClass.getName()
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" );
}
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wa c =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationCont ext) BeanUtils .instantiateCl ass(contextClas s);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment()) ;
wac.setParent(parent) ;
String configLocation = getContextConfigLocation() ;
if (configLocation != null ) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocati on);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationCon text(wac);
return wac;
}
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationCo ntext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if(ObjectUtil s.identityToSt ring(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The applicatio n context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on availa ble informati on
if (this.contextI d != null ) {
wac.setId (this .contextI d);
}
else {
// Genera te defau lt id. ..
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContex t.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFI X
ObjectUtils .getDisplayStri ng(getServletContext().getContextPath()) '/'
getServletName()) ;
}
}
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext( ));
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig()) ;
wac.setNamespace(getNamespac e());
wac.addApplicationListener( n ew SourceFilteringListener(wac , new ContextRefreshListener())) ;
// The wac environment 's #initPropertySources w ill be called in any case when the context
// isrefreshe d; do it eager ly here t o ensure s ervlet proper ty sources are in place fo r
// use in any post-processin g or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironmen t env = wac.getEnvironmen t();
if(e nv instan ceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment ) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironme nt) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext() ,
getServletConfig( ));
}
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac) ;
applyInitializers(wac) ;
wac.refresh();
}
从上面的代码中可以看出,在
configAndRefreshWebApplicationContext()方法中,调用 refresh()方法,这个是真正启动 IOC 容器的入口,后面会详细介绍。IOC 容器初始化以后,最后调用了DispatcherServlet 的 onRefresh()方法,在 onRefresh()方法中又是直接调用 initStrategies()方法初始化 SpringMVC 的九大组件:
/* *
* This implementation calls {@link #initStrategies}.
* /
@Override
protected void onRefresh (ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context) ;
}
/* *
* Initialize the strategy objects that thi s servlet uses.
* <p> May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
* /
// 初始化策略
protected void initStrategies (ApplicationContext context) {
// 多文件上传的组件
initMultipartResolver(context) ;
// 初始化本地语言环境
initLocaleResolver(context );
// 初始化模板处理器
initThemeResolver(context) ;
//handlerMapping
initHandlerMappings(context) ;
// 初始化参数适配器
initHandlerAdapters(context) ;
// 初始化异常拦截器
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context) ;
// 初始化视图预处理器
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context) ;
// 初始化视图转换器
initViewResolvers(context) ;
//
initFlashMapManager(context) ;
}